Do alkyl halides undergo hydrolysis. Alkyl halides undergo hydrolysis more easily than aryl halide because alkyl halide.

7 2 Sn2 Reaction Mechanism Energy Diagram And Stereochemistry Chemistry Libretexts
This has been attributed to two factors.

. It is because of the resonance of aryl halides which makes it stable and thus has less reactivity. 4 Why should care be exercised in handling. 1 Sterics and 2 Electronics.
So it is not stable. 3 More stable carbocations react slower than less stable carbocations. Whereas the alkyl halides doesnot have any resonance so to get stability it undergoes hydrolysisHere the aryl halide is already stable and so it doesnot react.
Carbocation formed from neopentyl halide is primary in nature. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. There are a lot of possibilities.
So if we say it undergoes directly. It is possible if we use as a nucleophile a weak base cyanide ion or alcohol. Why then do SN1 reactions that produce more stable carbocations occur faster.
For example allyl chloride reacts over 800 times faster than propyl chloride. 2 Why do primary alkyl halides typically undergo SN2 substitution reactions more rapidly than do secondary or tertiary alkyl halides. Nature of the carbon skeleton.
TERTIARY ALKYL HALIDES NEVER SHOW S N 2 REACTIONS. This question does not show any research effort. As more alkyl groups are added to the α carbon atom the substrate becomes less susceptible to S_N2 attack.
In this post we will talk about the S N 2 mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reactions. These reactions are divided in two main types. Whether an alkyl halide will undergo an S N 1 S N 2 E 1 or an E2 reaction depends upon a number of factors.
2 More stable carbocations react slower than less stable carbocations. The acid protonates the most basic atom in the reactant. Therefore when a primary alcohol reacts with a hydrogen halide it must do so in an SN2 reaction.
Recall that sp 2 halides and tosylates do not undergo SN2 reactions. Some of the more common factors include the natures of the carbon skeleton the solvent the leaving group and the nature of the nucleophile. 1 Why do primary alkyl halides typically undergo SN2 substitution reactions more rapidly than do secondary or tertiary alkyl halides.
Whether an alkyl halide will undergo an S N 1 or an S N 2 reaction depends upon a number of factors. Primary alkyl halides generally undergo S_N2 mechanisms because a 1 substrates have little steric hindrance to nucleophilic attack and b 1 carbocations are relatively unstable. Allyl halides are also reactive to S N 2 reactions ie allylic nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Some of the more common factors include the natures of the substrate carbon skeleton the solvent the leaving group and the nature of the nucleophile. Why then do SN1 reactions that produce more stable carbocations occur faster. These include the nature of the nucleophile and the type of solvent used.
The primary alkyl halides are undergoing the S N 2 reaction regardless of solvent. Only those molecules that form extremely stable cations undergo S N 1. Show activity on this post.
Keep in mind that the electronegativity order of hybridized carbons is cesp sp2 sp3. Although it undergoes rearrangement reaction to form tertiary one now it can undergo SN1 easily. Its noteworthy that allyl haldes react by nucleophilic substitution reactions much faster than similar alkyl halides.
There are a lot of possibilities. 27 Votes Primary alcohols cannot undergo SN1 reactions because primary carbocations are too unstable to be formed even when the reaction is heated Section 93. This reaction does not occur with tertiary alkyl halides because the nucleophilic attack is disabled.
One in which the nucleophilic attack and the. But with secondary alkyl halides is more difficult to achieve than with primary. As a reminder from the introduction to nucleophilic substitutions these are reactions where the nucleophile replaces the leaving group.
485 1095 Views. Tertiary alkyl halides are more reactive than secondary alkyl halides and primary alkyl halides do not react at all. There are several factors which determine whether substitution will be SN1 or SN2 and which also control the rate at which these reactions take place.
It is unclear or not useful.
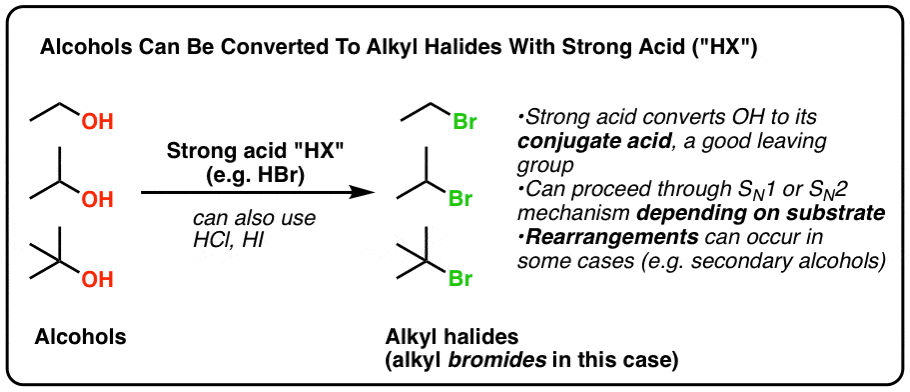
Making Alkyl Halides From Alcohols Master Organic Chemistry

Sn2 With Alkyl Halides Chemistryscore
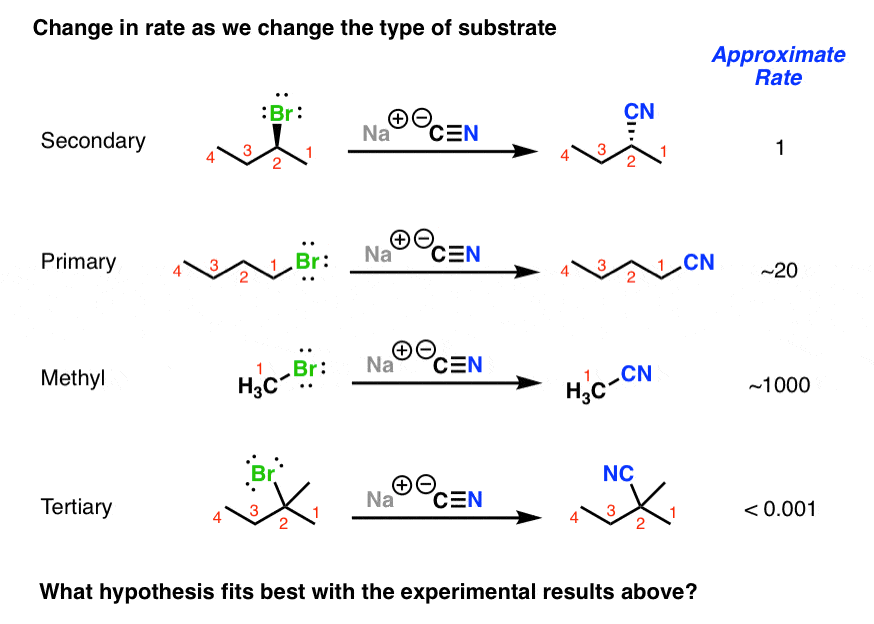
The Sn2 Reaction Mechanism Master Organic Chemistry
Why Do Primary Alkyl Halides Prefer Sn2 Reaction Mechanism For Nucleophilic Substitution Quora
0 Comments